How to get started in WordPress – (1/2)
As in any other software, it is always difficult to start and it has its learning curve. WordPress for the user who is going to use it is very comfortable and simple. But if someone tells you how to start in WordPress it will be even more so.
In this article I will teach you step by step how to use this powerful CMS (Content Manager) so that you can only manage it.
Contents
What is WordPress?
As I mentioned, WordPress is a content manager, its acronym in English is CMS (Content Manager System), acronyms with which this software is often referred to.
WordPress is licensed software LPG, which means that it is open source and it is also a project "community drive", which means that your community is the one that decides the course of this software. All updates, themes, plugins, support forum are their community behind.
How do I get started in WordPress
The first thing you should do to get started with WordPress is to know how to install it.
To download WordPress we must go to WordPress.org and we will go to get wordpress. Once we unzip it, we will upload everything to our FTP or local installation.
The installation of WordPress is known as the “5 minute installation” because of how easy and fast it is.
What do I need to install WordPress?
To install a WordPress we need:
- Database name
- Username
- Password
- Database server
- table prefix
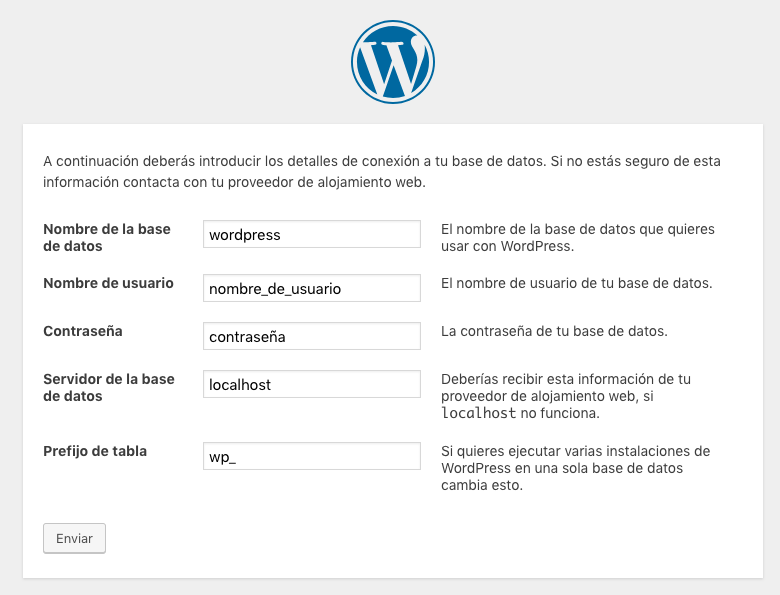
The first three fields will be provided by our hosting provider. In our administration panel we will go to the database section and create a new one. This will make it easier for usdatabase name","Username" and the "password«. In principle, we will leave the server in localhost.
El table prefix We must always change it for security reasons to a random prefix.
Once these data have been entered, we will go to a new page where we will enter the basic information of the site. On this page we will also create the first user (Administrator). A best practice would be to create a new administrator and delete this one.
All the information that we enter in this tab can be modified later. Once we have filled in everything we can enter our already functional WordPress.
First contact with WordPress
To enter the WordPress administrator the default path is www.mydomain.com/wp-admin. Here we will enter our username and password to enter.
Once we enter we will find the WordPress administration panel. In this panel we will see by default:
- Desktop
- Appetizers
- Media coverage
- Pages
- Comments
- Appearance
- Plugins
- Users
- Tools
- Settings
Each of these sections is responsible for an essential part of our website.
Desktop
On the desktop we can have a quick look at the web. In it we see different Widgets (complements) where we have, for example, the number of pages or entries, the latest comments, a quick draft for entries (this widget only saves them, it does not publish them), etc.
Widgets can be modified both in position and which appear on the desktop. Some plugins that we add will be able to add new widgets.
Appetizers
Here resides one of the lungs of WordPress, in this section is where we can write our entries (articles). We see that this section is made up of:
- All entries: as its name indicates, here we can see all the articles that we have written or have in draft.
- Add new: with this option we can create new entries.
- Categories: Categories are a form of organization for the articles on our blog and are hierarchical. Each article must not have more than one category.
- Tags: Tags, like categories, are a way of organizing articles. They do not have a hierarchy and we can put as many labels on the article as we want.
When writing entries we meet the editor Gutenberg, with which through blocks we can structure the content of our posts and layout them in a very comfortable and easy way.
If you want to learn more about how to use Gutenberg have a series of articles about it.
Categories
When we talk about the categories we have to see them as the great organizers of information on our blog. They are the folders that will organize the content. We must think carefully about the categories since they are going to index us.
each post DO NOT must carry more than one category since it would create duplicate content for us. Categories are hierarchical so there can be categories within categories
If we do not modify it by default, the route of a category will be the following:
mowomo.com/category/categoryname
We can edit this in «Settings > Permalinks«. For example, we at mowomo have:
mowomo.com/wordpress-development/categoryname

This is good to decide from the beginning because if we already have it indexed we would have to do 301 redirects.
Tags
Like the categories, the labels are used to sort the content with the difference that they are much more numerous and are not hierarchical. On the other hand, tags, unlike categories, some SEOs recommend not indexing. We can create labels more freely but having a good label structure will help to have a good organization of the content.
For example, if the Automotive category, the labels could be car, motorcycle, sports car, etc.
As with categories by default, the url of a tag is:
mowomo.com/tag/tagname
To change it we will go to «Settings > Permalinks»and like the categories we will have a field to enter the text we want.
Media coverage
In media is the section where we can upload our images, pdf, videos, etc. Everything referred to with audiovisual resources.
For each image we can edit the metadata of each one, we can edit quickly «Job Title","Legend","Alternative text" Y "Description«. We can also see data such as the «Size archive","Dimensions","Type of file","Upload date«.
we should always write alternative text to all the images Since it will help us in SEO and makes the web more accessible for people with disabilities since page readers use alternative text.
in Gutenberg the image block brings to be able to write the alternative text so you can see the importance of this field.
Pages
This section could be considered as one of the main sections of WordPress. Here we will create the web pages, from the home page to the legal page or our services, etc. Pages are hierarchical so we can have pages within pages.
Like the posts, it uses the Gutenberg editor to create the content that the pages will have.
Comments
Here we can see the comments that are written on our website if we have them active. It depends on the configuration that we have here, we can edit them, answer them, approve them, reject them or send them to spam.
I always recommend leaving them pending review which helps us clean up a lot of spam. To configure the comments you have to go to the section «Settings > Comments«.
Appearance
In the appearance section we find the Topics. A theme is what gives the appearance of our website. It is something that must be decided well since a badly constructed theme, even if it is very beautiful, can subtract more than contribute.
A good repository to search for themes is the WordPress repository itself. There we can find all kinds of themes and all free. When choosing a theme, look at its number of active installations and comments. A theme with bad ratings and few downloads is less recommended than a theme with many installs and good ratings.
Customize now
In customize we can edit other characteristics such as the «site identity"where we can edit"Site title","Short description" is "site icon» (in the site icon we can place the favicon, some themes use it to put the logo of the site).
En Menus we can choose and edit the menus. Although it is more convenient to edit it in the menus section than in the customizer. The widget just like the menus are easier to edit in your section than here in the customizer.
We also find the section cover settings where we can choose which page we use as the cover. We can choose betweenlast entries» Finding the blog page as the cover, or «static page» to choose one of the pages that we have created as a cover, at the same time we will have to choose a page to use as a blog.
Additional CSS It allows us to add CSS styles to our website. If you don't know CSS code, don't touch anything here.
Widgets
Widgets are elements that we can drag and drop on various sites such as the sidebar. These spaces will depend on our theme. There will be themes with more sites or others with less.
These items range from last entries, categories, files, text editor, HTML, navigation menus, etc.
They are very easy to edit and use, we just have to drag and edit it with what it asks for.
Menus
In this section we can create and edit the menus of our page. Once we have created one we can select where we are going to use it. The holes where we can use them will depend on the theme we use.
We can add any type of content to our menu, from pages to categories or personalized links. All we have to do is select what we want to add and add it to the menu.
Once added we can edit its order and its depth (sub menus).
So far the first part of how to start in WordPress, if you want to be aware to know when the second part comes out subscribe to our newsletter. In the second part of how to start in WordPress we will see:
- Plugins
- Users
- Tools
- Settings
When the second part is ready, I'll add the link to the second part here.
¡Subscribe to our newsletter and receive our offers, news and discounts directly to your email!









